用Python实现二叉树 遍历
树都是从一个主干根,然后往上分叉,每个枝杈又会分枝杈,而在计算机科学中,树则是可以看做一个倒挂的树,根在最上面,往下开叉,如下图:
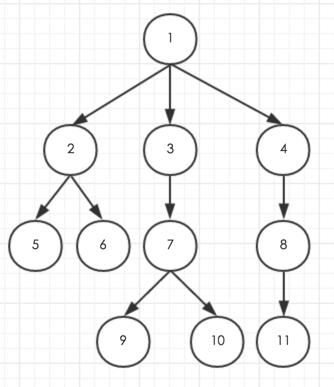
从这个图来看:
- 1节点就是根节点
- 从1分叉出了2、3、4节点。
- 2、3、4是1的孩子节点。
- 2、3、4互为兄弟节点。
- 1为2、3、4的父节点。
- 5、6是2的子节点。
- 这棵树深度是4(一共4层)
- 多棵树组成森林
二叉树
二叉树是每个节点最多有两个子节点的树,举个例子:
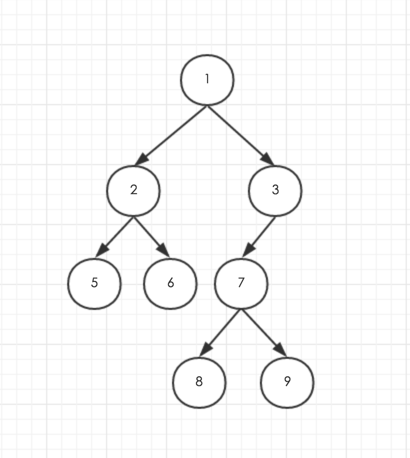
遍历
前序遍历(根左右)
还是以上图为例,前序遍历顺序是:
[1, 2, 5, 6, 3, 7, 8, 9]
中序遍历(左根右)
还是以上图为例,中序遍历顺序是:
[5, 2, 6, 1, 8, 7, 9, 3]
后续遍历(左右根)
还是以上图为例,后序遍历顺序是:
[5, 6, 2, 8, 9, 7 ,3, 1]
python实现二叉树
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
| class Node(object):
def __init__(self, index):
self.index = index
self.left_child = None
self.right_child = None
class Binary_tree(object):
def __init__(self, root):
self.root = root
def pre_travel(self, node):
if not node:
return
print(node.index, end=' ')
self.pre_travel(node.left_child)
self.pre_travel(node.right_child)
def mid_travel(self, node):
if not node:
return
self.mid_travel(node.left_child)
print(node.index, end=' ')
self.mid_travel(node.right_child)
def back_travel(self, node):
if not node:
return
self.back_travel(node.left_child)
self.back_travel(node.right_child)
print(node.index, end=' ')
node_dict = {}
for i in range(1, 10):
node_dict[i] = Node(i)
node_dict[1].left_child = node_dict[2]
node_dict[1].right_child = node_dict[3]
node_dict[2].left_child = node_dict[5]
node_dict[2].right_child = node_dict[6]
node_dict[3].left_child = node_dict[7]
node_dict[7].left_child = node_dict[8]
node_dict[7].right_child = node_dict[9]
tree = Binary_tree(node_dict[1])
print('前序遍历:')
tree.pre_travel(tree.root)
print('\n')
print('中序遍历:')
tree.mid_travel(tree.root)
print('\n')
print('后序遍历:')
tree.back_travel(tree.root)
print('\n')
|
输出:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| 前序遍历:
1 2 5 6 3 7 8 9
中序遍历:
5 2 6 1 8 7 9 3
后序遍历:
5 6 2 8 9 7 3 1
|

